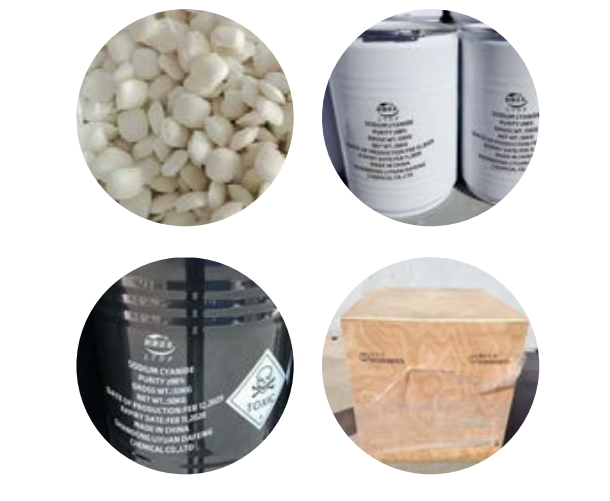
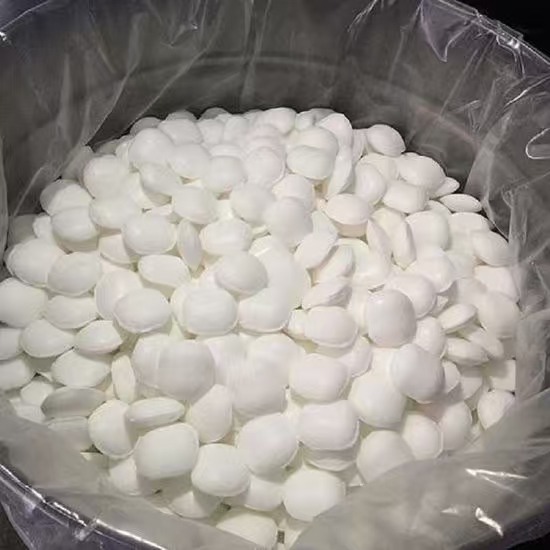
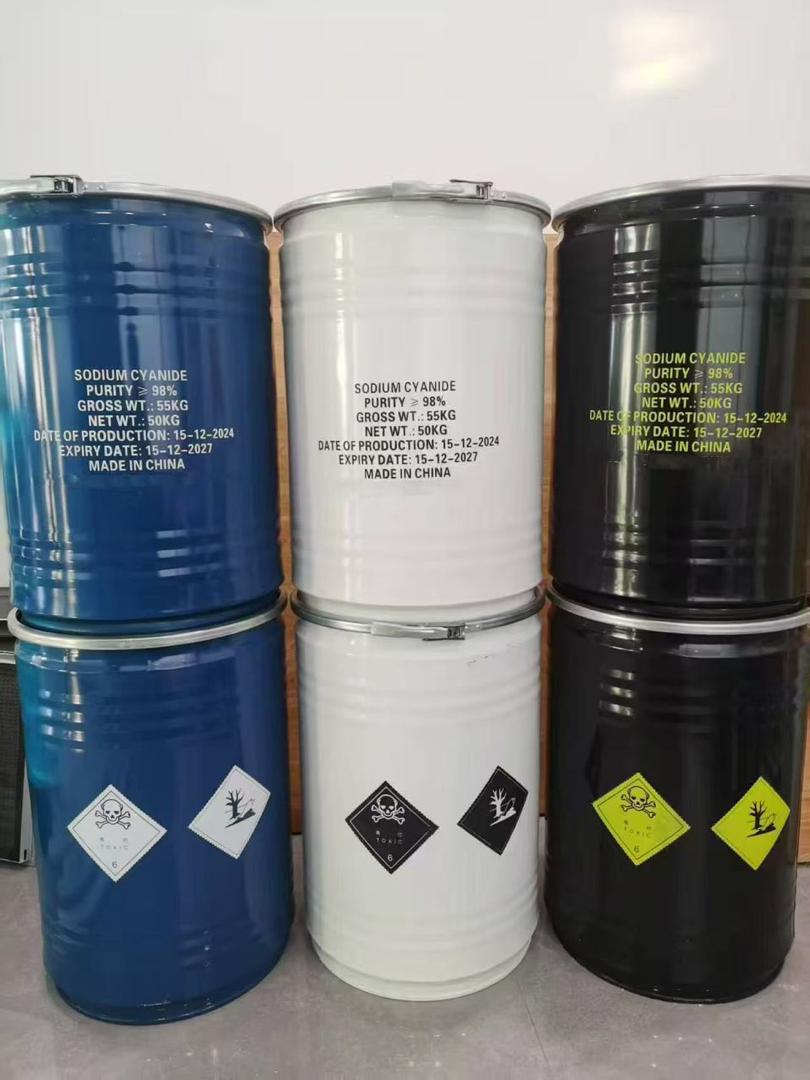
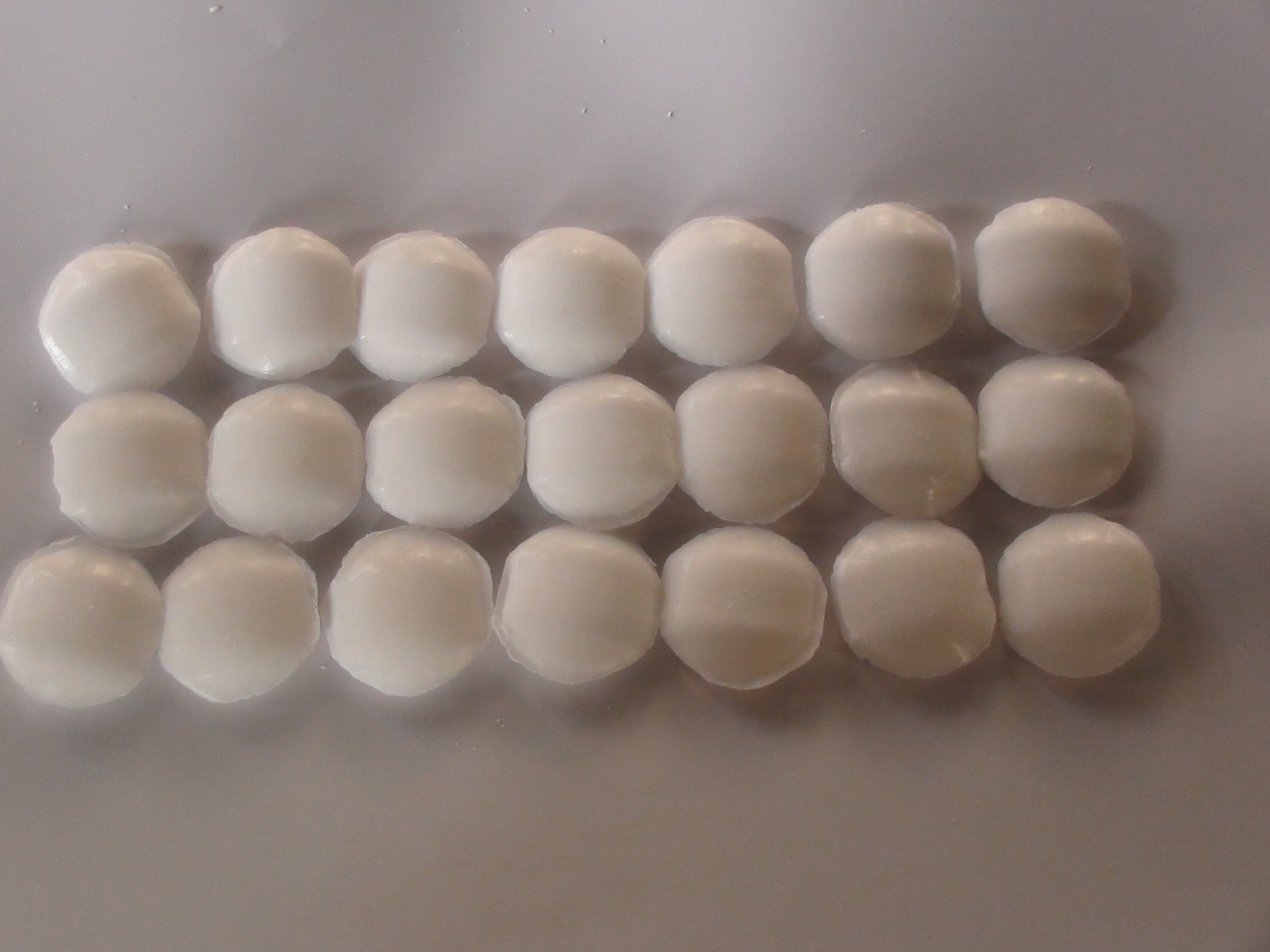
Sodium Cyanide
Sodium cyanide (NaCN)) is a highly poisonous, white crystalline solid that is rapidly fatal if swallowed, inhaled, or absorbed through open wounds. Its primary industrial use is in gold and silver mining to extract precious metals from low-grade ores.
Product Details
Product Features
Alternative names: Nutmeg, Nutmeg Sodium
CAS Number: 143-33-9
UN Hazardous Materials Identification Number: 1689
Sodium cyanide is an inorganic compound belonging to the cubic crystal system. Its chemical formula is NaCN. It is prone to deliquescence, has a faint bitter almond odor, is highly toxic, and can cause poisoning and death even with a small amount of contact with skin wounds, inhalation, or ingestion. Its melting point is 563.7℃ and its boiling point is 1496℃. It is highly soluble in water and readily hydrolyzes to form hydrogen cyanide. The aqueous solution is strongly alkaline and is an important basic chemical raw material. It is used in basic chemical synthesis, electroplating, metallurgy, and organic synthesis for medicine, pesticides, and metal treatment as a complexing agent and masking agent.
It is used as a quenching agent for various types of steel in the mechanical industry. In the electroplating industry, it serves as a major component for plating copper, silver, cadmium and zinc, etc. In the electroplating solution, it can reduce the anode polarization effect, ensure the normal dissolution of the anode, stabilize the plating solution and enhance the cathode polarization effect, thereby achieving a uniform coating.
In the metallurgical industry, it is used for extracting precious metals such as gold and silver.
In the chemical industry, it is used to produce various inorganic cyanides and raw materials for hydrogen cyanide, and is also employed in the manufacture of organic glass, various synthetic materials, nitrile rubber, and copolymers of synthetic fibers.
It is used in the dye industry to produce trichlorocyanine (an intermediate for reactive dyes, and also a raw material for the production of whitening agents).
It is used in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of compounds such as methyl cyanoacetic acid and diethyl malonic acid.
In the textile industry, it is used as a mordant agent, and is also employed in the liquid carburizing and nitriding of steel. The important inorganic cyanides produced directly from sodium cyanide mainly include sodium hematin, potassium hematin, potassium cyanide, zinc cyanide, barium cyanide, copper cyanide, sodium thiocyanate, potassium thiocyanate; organic cyanides include cyanic acid, propionitrile, methionine, cyanobenzyl, trichlorocyanine, etc. The main products produced by the reaction of sodium cyanide to produce hydrogen cyanide and then further processing include: methyl methacrylate, methyl butacrylate, methacrylic acid, azobisisobutyronitrile, azobisisodecynitrile, secondary amino triethylenetetramine, hydroxyacetonitrile, etc.
Product Applications
Sodium cyanide is mainly used in metallurgy (such as gold mining), electroplating, organic synthesis, and pesticide production. Due to its extreme toxicity, it requires strict management; it should be kept away from acids and nitrates and stored in a dry, well-ventilated environment.
Beyond gold mining, sodium cyanide has several other industrial applications:
⋅Electroplating: Used in cyanide baths to electroplate metals like platinum, gold, and silver.
⋅Chemical Feedstock: A strong nucleophile used in organic synthesis to produce nitriles and other specialty chemicals, including some pharmaceuticals.
⋅Metal Treatment: Used in case-hardening of iron and steel and metal polishing.
⋅Niche Uses: Historically used in entomology collecting jars to kill insects rapidly and, illegally, in cyanide fishing.
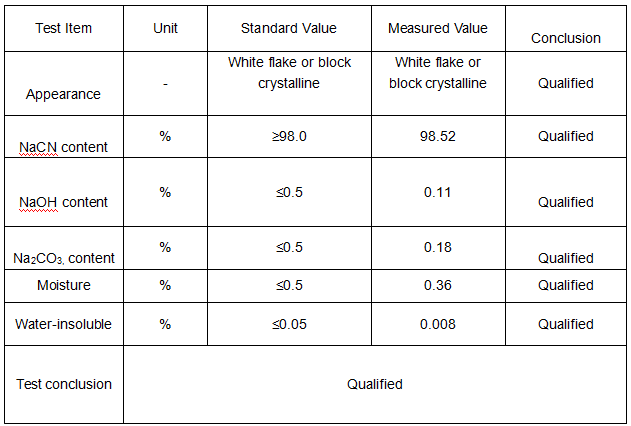
Product Parameters
Related Products
Online Message